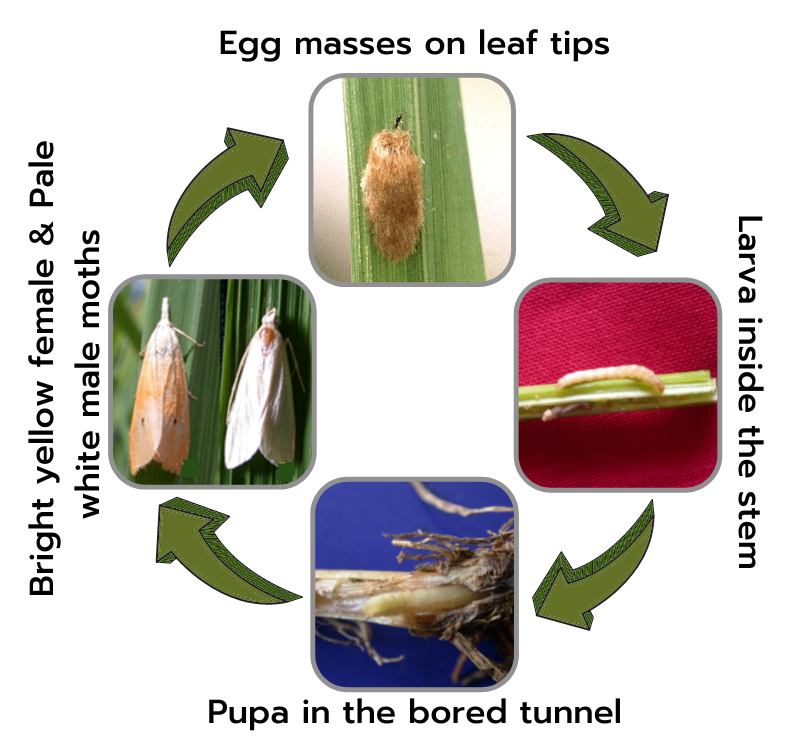
Female moth is bright yellow in colour with conspicuous black spot in the centre of forewings. Abdomen is wide with a tuft of hairs. Male moth is pale yellow in colour with slender abdomen. Males are smaller in size than female moths.
Eggs are laid in masses, usually on leaf tips and covered with hairs. Eggs hatch in about 5-10 days.
Immediately after hatching, first instar larvae disperse with the help of silken threads. Initially they feed by scraping on the green matter and later bore into the stem above the water level. Larvae are solitary in nature and feed on the internal contents of stem. Larval period ranges between 30 - 46 days.
Larva pupates inside the bored stem. Pupal period takes about 6-10 days. It takes about 52 - 71 days for complete development.

Damage is observed throughout the crop growth period. During vegetative phase, immediately after hatching, larvae bore into the stem resulting in the death of central whorl. This is known as "Dead heart". Central whorl of affected tillers turns brownish and dries out while the lower leaves remain green and healthy. At reproductive phase, the damage is characterized by whitish empty panicles that stand erect and are very conspicuous in field. These are called 'white ears'. Infestation also results in partial chaffiness and ill-filled grains in some cases.
Deep summer ploughing to expose the larvae.
Timely planting to avoid the pest attack, as late planting leads to heavy incidence.
Clipping the tips of leaf blades of seedlings before transplanting.
Installation of Pheromone traps @ 3 traps per acre monitoring of yellow stem borer. When the moth catches in these pheromone traps exceeds 35 per week, management practices have to be initiated.
Trap crop - Grow pusa basmati variety in one line after every 9 lines of main crop to reduce the stem borer damage.
Grow cowpea, marigold, soybean, green gram or any flowering plant on bunds to attract and conserve the natural enemies.
Inundative release of egg parasitoids, Trichogramma japonicum. Releases are made five to six times @ 1,00,000 per hectare starting from 15 days after transplanting. Tricho cards containing 1000 parasitised eggs stapled to the underside of leaves at 100 points uniformly distributed across 1-hectare area.
When there are 5% dead hearts or 1 egg mass per square meter or one female moth per square meter, following chemicals can be applied:
Cartap hydrochloride 4G @ 8 kg per acre (or) Chlorantraniliprole 0.4G @ 4 kg per acre.
Spray any of the following chemicals:
Cartap hydrochloride 50 WP/SP @ 400 g (or) Chlorantraniliprole (Rynaxypyr) 18.5 SC @ 60 ml (or) Acephate 75 WP @ 250 g per acre.